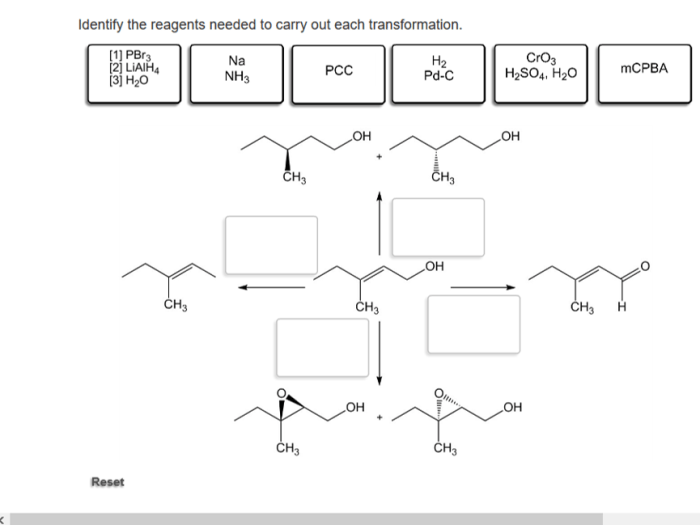
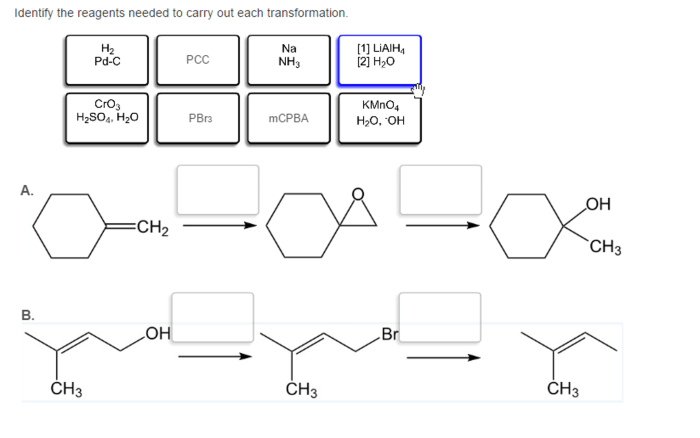
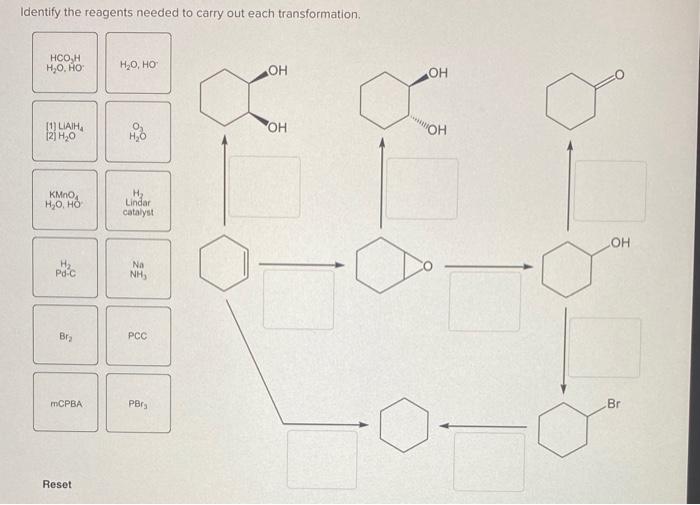
In the realm of organic chemistry, identifying the appropriate reagents for specific transformations is a crucial step towards successful synthesis. This guide explores the principles and considerations involved in reagent selection, providing a comprehensive understanding of how to identify the reagents needed to carry out each transformation.
Factors influencing reagent choice, such as selectivity, reactivity, and cost-effectiveness, are discussed in detail, along with practical methods for preparing and handling common reagents. By delving into the intricacies of reagent identification, chemists can optimize their synthetic strategies and achieve desired outcomes with greater precision.
Reagent Identification
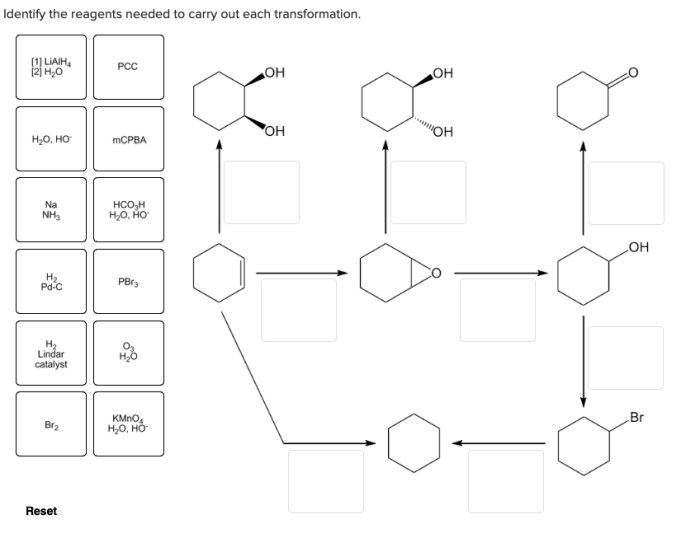
Reagents are chemical substances that are used to bring about a chemical reaction. The choice of reagents for a given transformation is influenced by a number of factors, including the selectivity, reactivity, and cost-effectiveness of the reagent.
The following table provides examples of organic transformations, their reactants and products, and the reagents needed to carry out each transformation:
| Transformation | Reactant(s) | Product(s) | Reagents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleophilic substitution | Alkyl halide | Alcohol | Hydroxide ion |
| Electrophilic addition | Alkene | Alkyl halide | Hydrogen halide |
| Radical addition | Alkene | Alkyl radical | Radical initiator |
| Oxidation | Alcohol | Ketone | Potassium permanganate |
| Reduction | Ketone | Alcohol | Sodium borohydride |
Clarifying Questions: Identify The Reagents Needed To Carry Out Each Transformation.
What are the key factors to consider when selecting reagents for a chemical transformation?
Selectivity, reactivity, and cost-effectiveness are the primary factors that influence reagent choice.
How can I prepare common reagents safely and effectively?
Step-by-step procedures for preparing reagents such as Grignard reagents and organolithium compounds are provided, along with safety precautions.
What techniques are used to characterize reagents and ensure their purity?
NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and elemental analysis are common techniques for reagent characterization.