Alzheimer’s disease advanced stages hesi case study – Delving into the intricate world of Alzheimer’s Disease Advanced Stages: A Comprehensive Examination for HESI Case Study, this analysis unravels the complexities of this neurodegenerative condition, exploring its profound impact on cognitive function, daily living, and caregiving responsibilities. Through a meticulous examination of clinical manifestations, disease progression, and therapeutic interventions, this study illuminates the challenges faced by individuals and their caregivers, providing invaluable insights for healthcare professionals and students alike.
As Alzheimer’s disease progresses to its advanced stages, a cascade of cognitive and behavioral symptoms emerges, significantly impairing an individual’s ability to perform daily activities. This study meticulously examines the progression of these symptoms, from mild cognitive decline to severe impairments in memory, language, and executive functioning.
Furthermore, it explores the impact of these symptoms on daily functioning, highlighting the challenges individuals face in areas such as self-care, mobility, and communication.
Clinical Manifestations of Alzheimer’s Disease Advanced Stages: Alzheimer’s Disease Advanced Stages Hesi Case Study
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects the brain’s memory and cognitive functions. As the disease progresses to its advanced stages, the symptoms become more severe and debilitating.
Cognitive Symptoms
In advanced AD, cognitive impairments become pronounced and pervasive. Individuals may experience:
- Severe memory loss, affecting both short-term and long-term memories
- Difficulty recognizing familiar faces and places
- Impaired judgment and decision-making abilities
- Reduced comprehension and language skills
- Disorientation and confusion
Behavioral Symptoms
Behavioral symptoms also become more common in advanced AD. These may include:
- Agitation, restlessness, and wandering
- Mood swings and irritability
- Sleep disturbances
- Hallucinations and delusions
- Loss of inhibitions
The progression of symptoms from mild to severe stages of AD is gradual but relentless. As the disease progresses, individuals become increasingly dependent on others for assistance with daily activities and personal care.
Impact on Daily Functioning
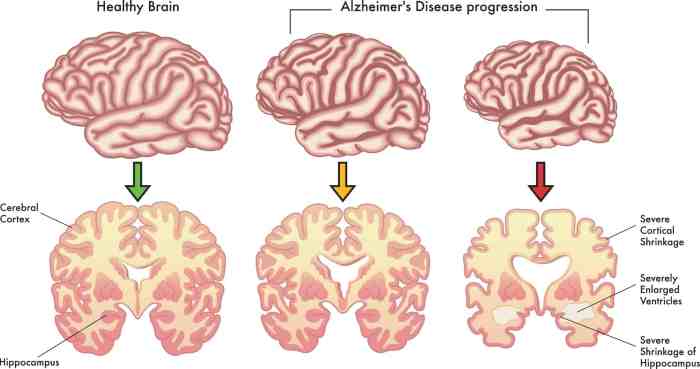
The cognitive and behavioral symptoms of advanced AD significantly impact daily functioning. Individuals may face challenges in:
Self-care
Dressing, bathing, and toileting become difficult or impossible.
Mobility
Walking, balance, and coordination are impaired, leading to increased risk of falls.
Communication
Speech becomes limited or unintelligible, making it difficult to express needs or engage in conversations.
Eating
Individuals may have difficulty swallowing or lose their appetite.
Social interaction
They may withdraw from social activities and experience difficulty recognizing or interacting with loved ones.These challenges require extensive assistance and support from caregivers, family members, or healthcare professionals.
Caregiving for Individuals with Advanced Alzheimer’s Disease
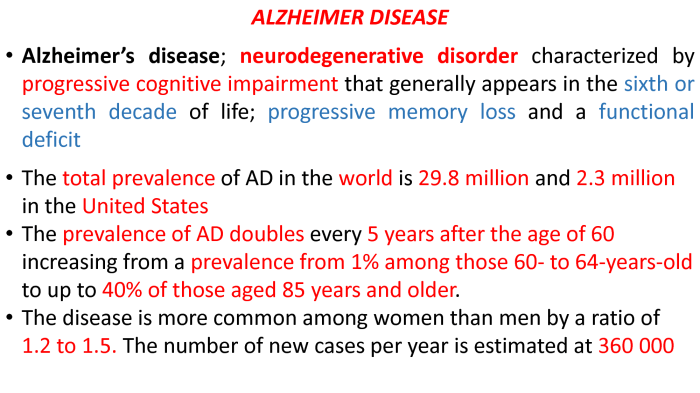
Caring for someone with advanced AD is physically and emotionally demanding. Caregivers need to provide assistance with daily activities, manage behavioral challenges, and promote well-being.
Physical Care
- Assist with bathing, dressing, toileting, and feeding.
- Ensure adequate nutrition and hydration.
- Monitor for and prevent falls and other safety concerns.
Behavioral Management, Alzheimer’s disease advanced stages hesi case study
- Respond to agitation and wandering calmly and reassuringly.
- Provide a safe and structured environment.
- Engage in activities that provide stimulation and enjoyment.
Promoting Well-being
- Maintain a positive and supportive attitude.
- Encourage social interaction and meaningful activities.
- Provide emotional support and respite for caregivers.
Caregiving for individuals with advanced AD requires patience, understanding, and a deep commitment to providing comfort and dignity.
FAQ Summary
What are the key cognitive symptoms of advanced Alzheimer’s disease?
Advanced Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by severe cognitive impairments, including memory loss, language difficulties, impaired judgment, and disorientation.
How does Alzheimer’s disease impact daily functioning in advanced stages?
In advanced stages, individuals may experience significant difficulties with self-care activities, mobility, and communication, requiring assistance and support from caregivers.
What are the challenges faced by caregivers of individuals with advanced Alzheimer’s disease?
Caregivers of individuals with advanced Alzheimer’s disease face physical and emotional demands, including managing behavioral challenges, providing assistance with daily activities, and ensuring the well-being of their loved ones.
What medical interventions are available for advanced Alzheimer’s disease?
Medications such as cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine are used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, while non-pharmacological interventions like cognitive stimulation and music therapy provide additional support.
What is the prognosis for individuals with advanced Alzheimer’s disease?
Advanced Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive condition with a typically poor prognosis. Life expectancy varies, but individuals may survive for several years after diagnosis.