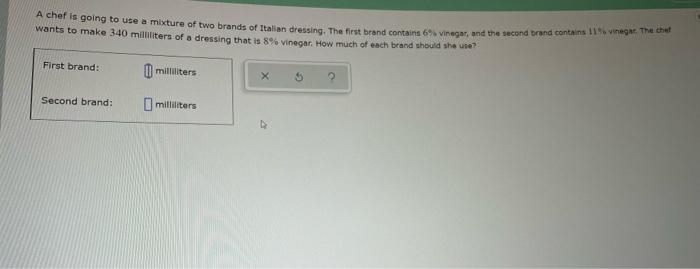
A chef is going to use a mixture, whether it’s a simple vinaigrette or a complex emulsion. Mixtures are a fundamental part of cooking, and they can be used to create a wide variety of flavors, textures, and appearances. In this article, we will explore the different types of mixtures used in cooking, the ingredients that go into them, and the techniques used to mix them.
We will also discuss the role of mixtures in culinary applications and the challenges that chefs face when working with them.
Mixtures are a combination of two or more ingredients that are not chemically bonded. They can be classified into two main types: homogeneous and heterogeneous. Homogeneous mixtures are those in which the ingredients are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. Examples of homogeneous mixtures include solutions, suspensions, and colloids.
Heterogeneous mixtures are those in which the ingredients are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture. Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include mixtures of solids, liquids, and gases.
1. Introduction to Mixture Use in Cooking: A Chef Is Going To Use A Mixture
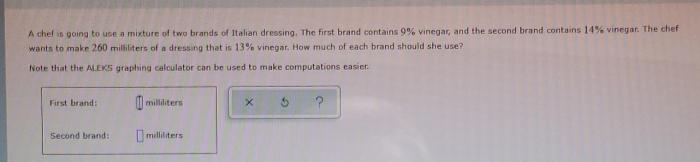
Mixtures play a pivotal role in the culinary arts, providing chefs with a means to create complex flavors, textures, and appearances in their dishes. Mixtures are defined as combinations of two or more ingredients that are not chemically bonded but retain their individual identities.
They can be categorized into various types, including marinades, batters, sauces, and doughs.
Common mixtures used in various cuisines include: marinades (e.g., teriyaki sauce, Italian dressing), batters (e.g., pancake batter, tempura batter), sauces (e.g., béchamel sauce, tomato sauce), and doughs (e.g., bread dough, pizza dough).
2. Ingredients and their Interactions
Mixtures can be composed of a wide range of ingredients, including liquids (e.g., water, milk, oil), solids (e.g., flour, sugar, salt), and gases (e.g., air, carbon dioxide). The interactions between these ingredients are influenced by their physical and chemical properties, such as solubility, polarity, and reactivity.
Ingredient ratios and proportions are crucial for achieving the desired texture, flavor, and appearance of a mixture. Altering the proportions of ingredients can significantly impact the outcome of the mixture.
3. Techniques for Mixing, A chef is going to use a mixture
Chefs employ various techniques to mix ingredients, each with its advantages and disadvantages. These techniques include:
- Stirring: A simple but effective method that involves using a spoon or whisk to combine ingredients.
- Whisking: A more vigorous method that incorporates air into the mixture, creating a lighter texture.
- Beating: A technique used to create a smooth, homogeneous mixture by using a whisk or electric mixer.
- Folding: A gentle technique used to combine delicate ingredients without overmixing.
- Kneading: A technique used to develop gluten in doughs, resulting in a chewy texture.
4. The Role of Mixtures in Culinary Applications
Mixtures serve various functions in cooking, including:
- Flavor enhancement: Mixtures such as marinades and sauces add flavor to food.
- Texture modification: Mixtures such as batters and doughs create different textures in food.
- Appearance enhancement: Mixtures such as glazes and coatings add a glossy or matte finish to food.
Examples of dishes that rely heavily on mixtures include: marinated grilled chicken, tempura-fried vegetables, pasta with tomato sauce, and bread.
5. Challenges and Troubleshooting
Chefs may encounter challenges when working with mixtures, such as:
- Overmixing: Overmixing can lead to a tough or dense texture.
- Undermixing: Undermixing can result in an uneven distribution of ingredients.
- Separation: Mixtures can separate due to differences in density or polarity.
Troubleshooting tips include:
- Mix ingredients only until just combined.
- Use a whisk or electric mixer to ensure thorough mixing.
- Add an emulsifier (e.g., egg yolk, mustard) to prevent separation.
6. Advanced Mixture Techniques
Professional chefs employ advanced mixture techniques to create innovative and complex dishes. These techniques include:
- Sous vide: A technique that involves cooking food in a sealed vacuum-packed bag at a precise temperature.
- Molecular gastronomy: A field that explores the science behind cooking and utilizes techniques such as spherification and emulsification.
- Fermentation: A process that involves the use of microorganisms to transform food ingredients, creating new flavors and textures.
FAQ Summary
What are the different types of mixtures used in cooking?
There are two main types of mixtures used in cooking: homogeneous and heterogeneous. Homogeneous mixtures are those in which the ingredients are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. Examples of homogeneous mixtures include solutions, suspensions, and colloids. Heterogeneous mixtures are those in which the ingredients are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture.
Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include mixtures of solids, liquids, and gases.
What are the ingredients that go into mixtures?
The ingredients that go into mixtures can vary depending on the type of mixture being made. However, some common ingredients include water, oil, vinegar, sugar, salt, and spices.
What are the techniques used to mix ingredients?
There are a variety of techniques that can be used to mix ingredients. Some common techniques include stirring, whisking, beating, and blending.